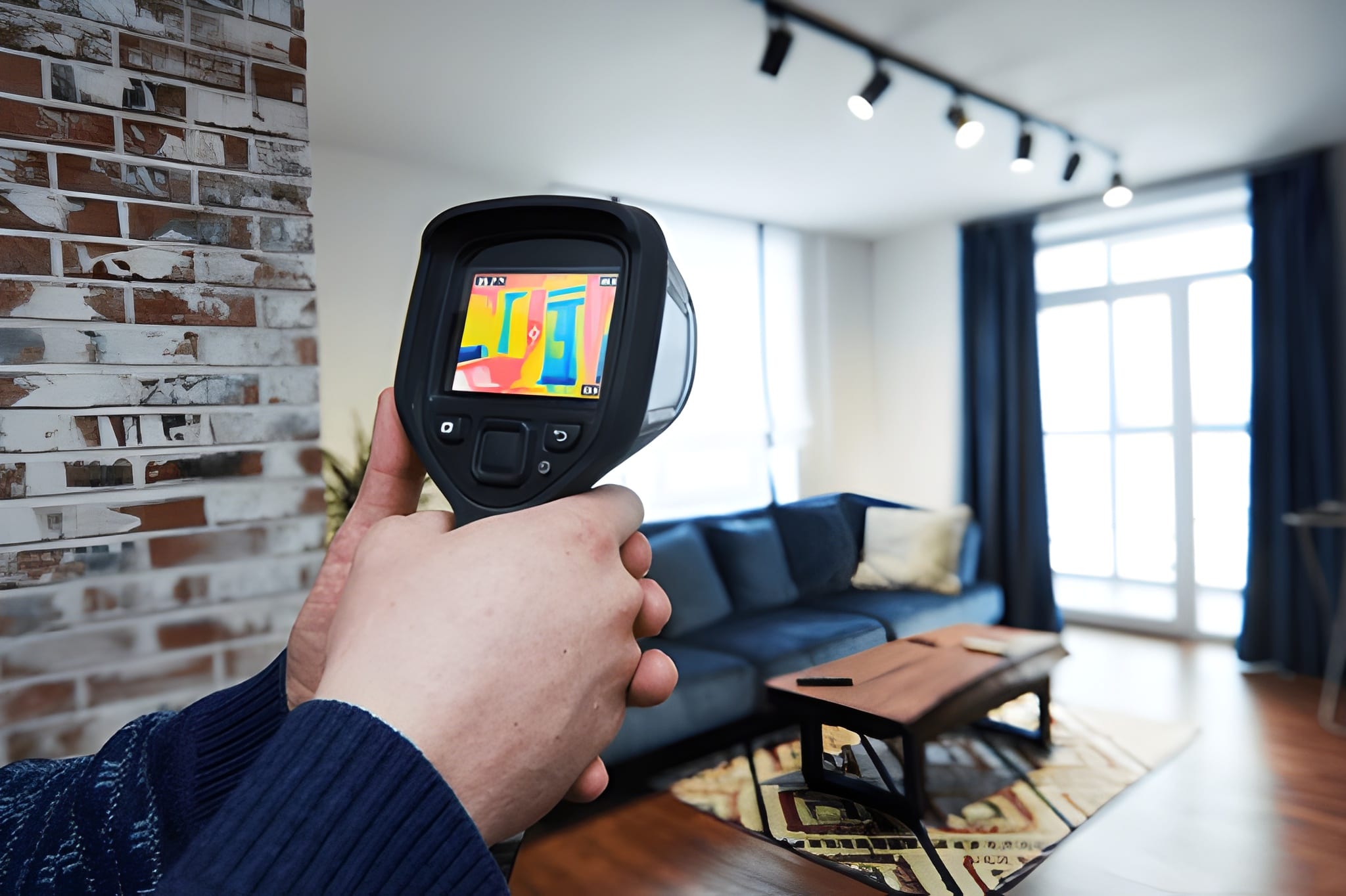
It can feel rather overwhelming stepping into the world of thermal imaging, as each model ranges under its different specifications and price ranges. The question remains solid for each of these users, whether a home inspector for moisture intrusion, an electrician troubleshooting a faulty circuit, or an enthusiast looking to navigate in the dark outdoors: what really distinguishes a decent tool from something that is absolutely game-changing? The answer is not one magic bullet but a number of features working together to make the critical clarity, accuracy, and actionable data possible. Understanding these key characteristics is the first step to the detection of the best thermal imaging camera that will fit specific needs and budgetary considerations. The whole premise revolves around matching the tool to the task, ensuring you are armed with a device that empowers you, rather than just impresses you.
The Heart of the Image: Resolution Is King
Of the many specifications that need to be considered when evaluating thermal cameras, the two most important are the detector resolution and the display resolution. The number of pixels to capture infrared data is associated with the number of pixels in the detector (or sensor) resolution: the higher the detector resolution, such as 320×240 or 640×480, the better page distinction the camera will have and the sharper the resultant thermal image. Important when you’re trying to find very tiny differences in temperature, such as that from a single overheating component among a crowded circuit board or between stud locations on a wall. The display resolution is the screen on which this image is presented. A high-resolution display (e.g., 640×480 or better) ensures that the rich data from a good sensor is presented with clarity, without pixelation. The camera captures a good-quality image, which looks bad when viewed on a high-resolution display: a typical case when the display has a high resolution but the sensor has a low resolution. Always have in hand a higher detector resolution.
Thermal Sensitivity: Seeing the Subtle Details
Thermal sensitivity can be understood as Noise Equivalent Temperature Difference—this is measured in milliKelvins (mK)—and refers to the camera’s ability to detect hot spots characterized as small differences in temperature. Some designers may use values such as <50 mK, with lower numbers indicating a more sensitive camera. This is huge because it enables a camera with high thermal sensitivity to see thermal patterns too delicate to be distinguished by a less sensitive model. For example, it may reveal the faint heat signature of a leak spreading very slowly under a floor or an almost-normal but slightly overloaded wire before it decides to become critical. This is all part of predictive maintenance and building diagnostics, which is really what their purpose is: catching something early.
Key Factors in Choosing the Best Thermal Imaging Camera
Beyond the core specs of resolution and sensitivity, several other factors significantly impact the camera’s usability and effectiveness in the field.
1. Palette Selection and Analysis Tools
A thermal camera doesn’t just show a picture; it visualizes data. The color palette you use (e.g., Ironbow, Rainbow, or Grayscale) can make certain details easier to interpret. The best cameras offer multiple palettes to suit different environments and user preferences. Furthermore, built-in analysis tools are essential. Look for features like
- Spot Meter: Measures the temperature at a single, specific point.
- Area Box: Shows the min, max, and average temperature within a defined rectangle.
- Isotherms: Highlights all areas above or below a set temperature threshold, perfect for quickly identifying hotspots or cold spots.
2. Lens Options and Field of View
In the hands of a thermal view, it determines how much of an area is captured at any specific point. A wider field of view (FOV), usually measured in degrees, is handy for such situations as scanning large areas like the ceiling or an electrical panel. A standard FOV or narrow FOV, on the other hand, allows users to observe the target from the farthest possible distance and is ideal for high-voltage inspection work or observing distant wildlife. Professional cameras with interchangeable lenses will afford more flexibility.
3. Durability and Design
A thermal camera is expected to work in an extreme environment—dusty construction sites or wet rooftops. Going for a rugged build that can withstand a drop from a certain height (usually MIL-STD-810G) with a good Ingress Protection (IP) rating against water and dust (say, something like IP54) becomes a good investment. Also, ergonomics: How friendly is it to hold with one hand? How easy are the controls to use, even with gloves?
4. Software and Connectivity
Modern thermal cameras are data hubs. Wi-Fi connectivity allows for video streaming and for images to be transferred directly to a smartphone or tablet. Companion apps can provide remote control, advanced reporting, and annotation features, enabling the conversion of a raw thermal image into a polished report for the client. The ability to overlay a thermal image on a standard digital photo (MSX or Picture-in-Picture) provides vital visual context—demonstrating precisely where the thermal anomaly is located.
5. Battery Life
A dead battery in the midst of an active job can be most disheartening. Look for a camera with a battery life that meets your workflow needs. Many models currently utilize interchangeable rechargeable lithium-ion packs, allowing you to carry spare batteries for all-day use without needing to plug in.
Final Thoughts
By definition, the best thermal camera will feel one with your expertise: simple, clear, and right there when you need it. When weighing features (beginning with a high-resolution detector, excellent thermal sensitivity, and powerful analysis tools), you sift through the marketing messages and come into an informed choice-making process. After all, you are looking for a trustworthy assistant in diagnostic and discovery work, and if you keep this blend of performance and practicality in focus, the best thermal imaging camera to help you light the dark challenges in your work will surely be found.