Cookies are tiny bits of information kept on a user’s browser. They assist websites in recalling details about users, like login information or preferences, even when the browser is closed. When a user visits a website, the server has the ability to transmit a cookie with a distinctive identifier that the browser keeps.
During later visits, the browser transmits this identifier to the server, enabling it to identify the user. Cookies are essential in web applications as they provide smooth functionality and personalized experiences. If you want to learn how cookies and sessions work in real applications, consider enrolling in the Full Stack Developer Course in Mumbai at FITA Academy and gain practical knowledge.
Cookies can have different lifetimes. Session cookies are short-lived and are removed as soon as the browser is closed. Persistent cookies stay on the device for a designated duration, allowing websites to recognize users during subsequent visits. Cookies can also have various attributes like domain, path, and security flags to control where and how they are sent. Understanding cookies is a fundamental skill for building secure and responsive web applications.
What are Sessions
Sessions are server-side storage mechanisms that track user activity and state. Unlike cookies, which store data in the browser, session data is kept on the server, often linked to a unique session ID stored in a cookie.
When a user interacts with a website, the server can read the session ID from the cookie and fetch corresponding data from its storage. This approach allows sensitive information like authentication tokens to remain secure on the server. Sessions are widely used in login systems, shopping carts, and personalized dashboards.
Each session has a lifetime, which can be set to expire after a certain period of inactivity. The server manages this automatically, freeing resources when sessions are no longer active.
Sessions also help maintain the flow of interactions without repeatedly asking users to authenticate or input information. If you want to explore practical implementation and management of sessions, you can think about signing up for the Full Stack Developer Course in Kolkata and enhance your skills.
How Cookies and Sessions Work Together
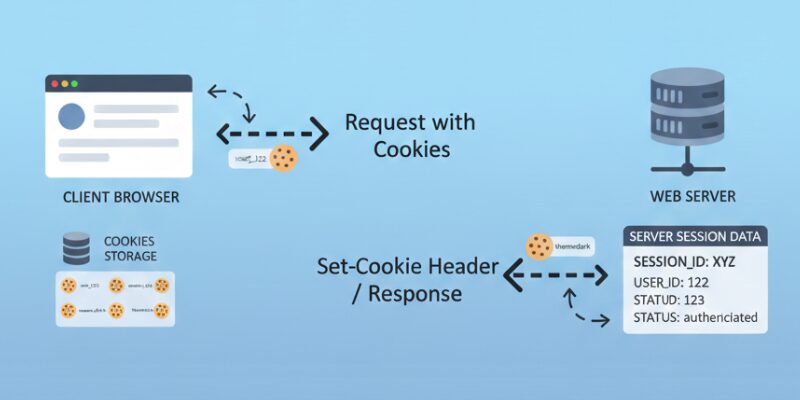
Cookies and sessions often work hand in hand. The cookie stores the session ID, while the server holds the actual session data. This combination allows websites to maintain user state efficiently and securely.
For example, when a user logs in, the server creates a session, stores relevant data, and sends a cookie containing the session ID. On subsequent requests, the server retrieves the session ID from the cookie and continues the user experience seamlessly. This mechanism also plays a role in security. Sensitive information stays on the server, reducing exposure to potential attacks, while the client only handles a small reference identifier.
By understanding this relationship, developers can design systems that balance convenience and safety effectively. For those eager to implement these concepts and become confident in full stack development, consider joining the Full Stack Developer Course in Delhi and take your knowledge further.
Also check: Scaling Full-Stack Apps for High Traffic







